使用udelay只有在傳入的參數是constant時才會檢查大小,成功就call __const_udelay
若不是constant則不會檢查大小,直接call __udelay(n),但delay的時間就不一定對了(算完後可能會overflow)
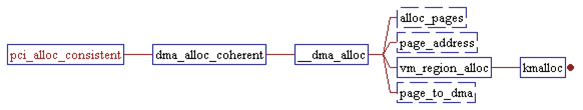
include/asm-arm/delay.h
implementations is in linux/arch/arm/lib/delay.S
#define MAX_UDELAY_MS 2
#define udelay(n) \
(__builtin_constant_p(n) ? \
((n) > (MAX_UDELAY_MS * 1000) ? __bad_udelay() : \
__const_udelay((n) * 0x68dbul)) : \
__udelay(n))
__builtin_constant_p: from GCC 4.3.0 Manual 5.49 Other built-in functions provided by GCC
— Built-in Function: int __builtin_constant_p (exp)You can use the built-in function
__builtin_constant_pto determine if a value is known to be constant at compile-time and hence that GCC can perform constant-folding on expressions involving that value. The argument of the function is the value to test. The function returns the integer 1 if the argument is known to be a compile-time constant and 0 if it is not known to be a compile-time constant. A return of 0 does not indicate that the value is not a constant, but merely that GCC cannot prove it is a constant with the specified value of the -O option.
 ),但是到1999年才被製作成動畫。而剛誕生的大嘴鳥就像醜小鴨一樣,一開始並不被日本森永製果看好,然而後來卻大受小朋友們的歡迎。
),但是到1999年才被製作成動畫。而剛誕生的大嘴鳥就像醜小鴨一樣,一開始並不被日本森永製果看好,然而後來卻大受小朋友們的歡迎。 !
! 。
。